Chemical Analysis
Notice: Undefined index: background_image in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Notice: Undefined index: background_image in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Notice: Undefined index: background_image in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Notice: Undefined index: background_image in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/mtalabor/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
TOTAL SOLUTION PROVIDER
IN MATERIAL TESTING AND ANALYSIS
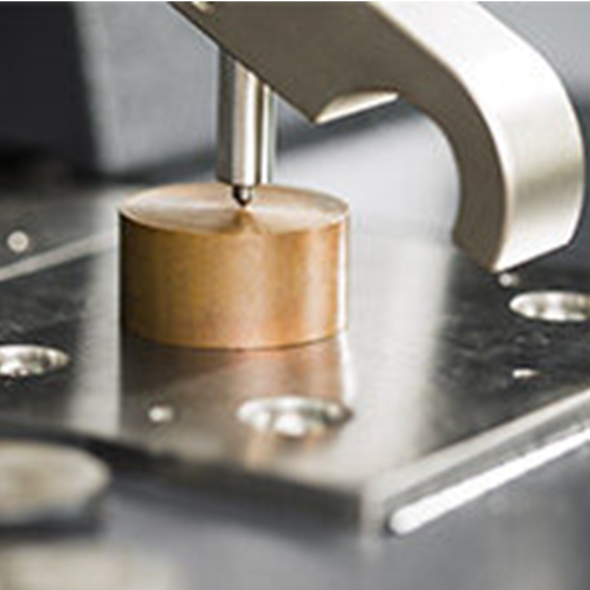
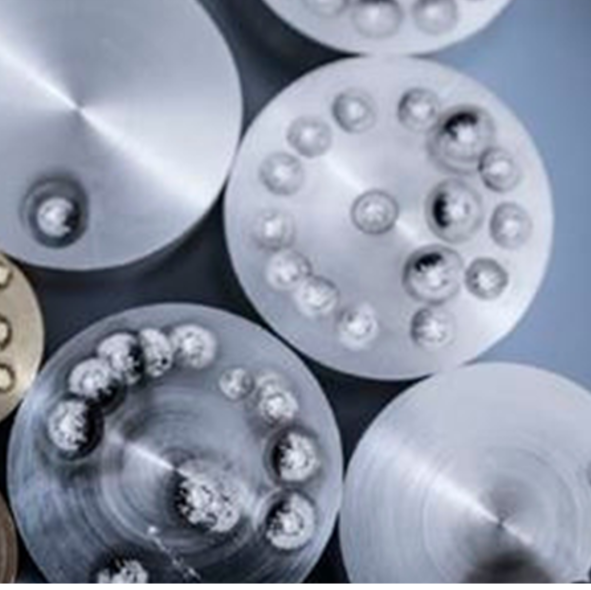
Spark Spectroscopy
Spark Spectroscopy enables material identification and characterization, typically in order to ensure the quality control of a material. This broad range of techniques can be used in a wide variety of applications, including to characterize trace impurities and measure unknowns
At MTA Laboratory were are providing elements identification up to 54 elements within a few minutes and all type of metal are capable being examined by using arc spark machine.
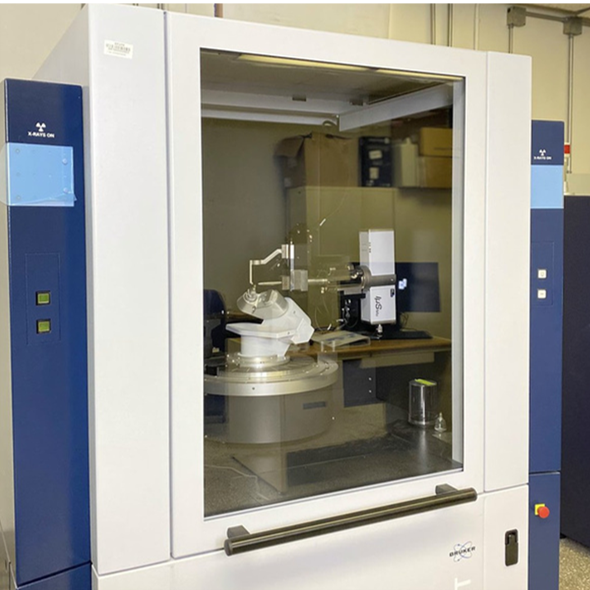





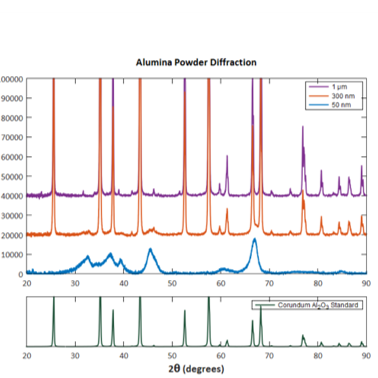
X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
- Determine the crystallographic structure of a material by irradiating a material with incident X-rays
- Measuring the intensities and scattering angles of the X-rays that leave the material.
- Differentiation between crystalline and amorphous material
- Determine structural properties such as lattice parameters, strain, grain size, epitaxy, phase composition and preferred orientation.
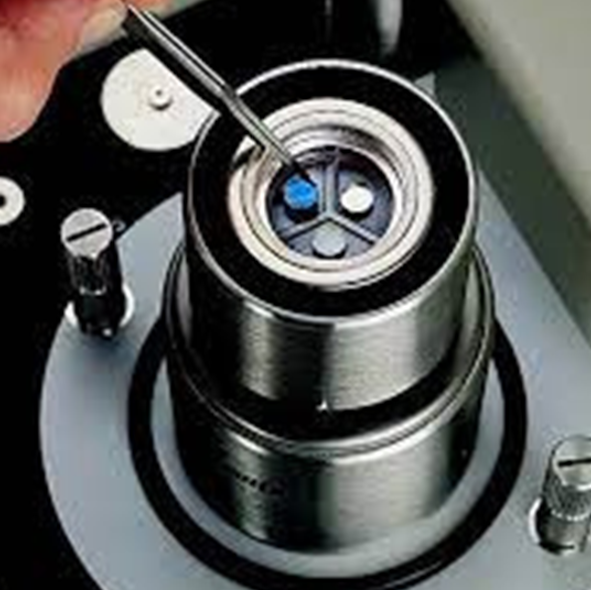
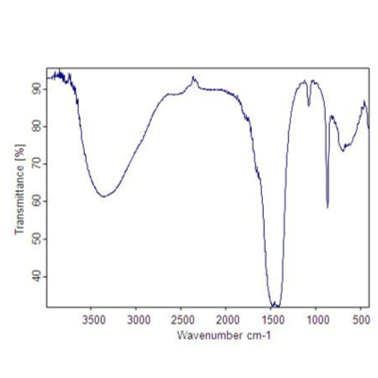
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
- Identify compounds and the general type of material being analysed when there are unknowns.
- Characterize unknown materials such as purity of inorganic sample especially in polymer composition (e.g., films, solids, powders, or liquids)
- Recognize contamination on or in a material (e.g., particles, fibres, powders, or liquids)



Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
- Difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference are measured as a function of temperature.
- Provide quantitative & qualitative information about physical and chemical changes that involve endothermic or exothermic processes.
- The main application of DSC is in studying phase transitions, such as melting, glass transitions, or exothermic decompositions.
